Cross-border payments are the lifeblood of today’s globalized economy. Driven by the increasing volume of international trade and commerce, tens of millions of payments take place each day, and that number is only set to go up.
In today’s digital economy, international payment systems are powering home-grown businesses like never seen before. A recent research says the volume of B2B payments will reach a whooping $124 trillion globally by 2028, marking a 40% increase from 2024 levels. And with cross-border transactions expected at this volume, firms need efficient, cost-effective payment solutions more than ever.
Check out this easy-to-follow guide to learn everything you possibly need to know about cross-border payments.
What are cross-border payments?
Cross-border payments are financial transactions where the payer and payee are located in different countries. The payments are made across international borders and usually require currency conversion. Here are some examples:
- A U.S. company paying its software development team in India
- An Indian manufacturer receiving payment from European retailers
- A funded startup receiving capital from its global headquarters
- A freelancer receiving payment from international clients
Types of cross-border payments
These transactions typically involve two main players: a domestic firm selling or purchasing goods and services and its foreign counterpart. Depending on the type of entities involved, here’s how cross-border payments can be classified:
1. B2B (Business to Business)
B2B cross border payments are the ones made from one business firm to another- think International trade payments, corporate investments, and treasury flows. These represent the largest volume, expected to reach $174.38 trillion by 2030.
2. B2C (Business to Consumer)
Payments from one business firm to a consumer- some examples include marketplace disbursements, government payouts, and refunds. This segment is relatively smaller and expected to reach $4.7 trillion by 2032.
3. C2B (Consumer to Business)
The C2B segment is projected to reach $5.6 trillion by 2030. Payments from a consumer to a business- These look like e-commerce purchases, mortgage payments for overseas property, and bill payments for education or healthcare.
4. C2C (Consumer to Consumer)
Payments between two consumers- common examples include remittances and payments to family members across borders. This segment is expected to reach $11.22 trillion by 2032.
How do cross-border payments work?
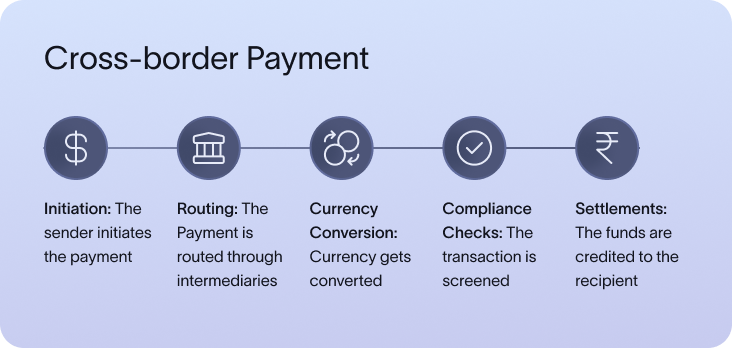
Behind every cross-border payment, there is a complex set of actions performed by various parties. The transaction starts from the initiator of the payment through the sending bank, moving through multiple intermediaries in between which finally routes to the receiving bank.
Here’s what happens in the background in a cross-border payment:
- Initiation: The sender makes a payment through their bank or payment provider. This step typically involves providing the necessary details, such as the recipient’s information and the amount to be sent.
- Routing: The payment moves through correspondent banks if using SWIFT or directly through payment platforms. Sometimes payments also movie through multiple intermediaries instead of just one.
- Currency Conversion: The sending currency is converted into the receiving currency, often at a markup. This process can result in additional costs, depending on the exchange rate applied and any hidden fees.
- Compliance Checks: Transactions undergo regulatory screening across jurisdictions, ensuring adherence to various legal requirements. This step helps mitigate risks related to money laundering, fraud, and terrorism financing.
- Settlement: The transaction is completed as the funds are credited to the recipient's account. The settlement process ensures that the recipient has access to the transferred amount, though delays may still occur depending on the system involved.
Banks and intermediaries have a key role in transaction costs and processing delays. Traditional cross-border payments usually involve the sending bank, 1-3 correspondent banks, and the receiving bank. Each institution performs its own checks and charges fees, adding to costs, delays, and inefficiencies that newer payment models aim to resolve by reducing or eliminating intermediaries.
Let’s paint a scenario where Maya, a writer based in Mumbai has completed a project for a company named Spark Ltd based in New York for $ 500.
Spark Ltd initiated a transaction via its bank, Bank Z, and sent the amount in $ to Bank A (Maya’s Bank).
Let us assume Bank Z does not have a direct relation with Bank A (Maya’s Bank) and is routed via 2 banks.
Bank D (correspondent to Bank Z) and Bank F (correspondent to Bank A)
Each intermediary processes the payment and charges a small handling fee.
Each bank will run compliance checks.
After a few days, the funds arrive in Maya’s account in INR (Bank A). The amount will be lower than actually transferred due to the handling and conversion fee charged.
Why do cross-border payments matter?
Now that we have a brief understanding of the process that cross border payments entail, let’s discuss why they really matter.
Today, even small businesses now routinely engage with international suppliers, partners, and customers. The COVID-19 pandemic has boosted this shift, with several firms looking to make their business global. For businesses of all sizes, the ability to send and receive international payments efficiently can be the difference between success and failure.
Impact on Different Types of Businesses
When it comes to international payments, every business has its own set of unique challenges. From procurement delays and supply-chain bottlenecks to stretched credit cycles, the challenges compound more when you have an unreliable payment process.
- Low fee payouts: For instance, startups looking to raise funds globally need reliable, cost-effective ways to transfer capital across borders. IT service exporters on the other hand require efficient systems to receive payments from international clients without excessive fees eating into their margins.
- Local Payments and Reach: E-commerce businesses also need to offer localized payment methods to customers worldwide while managing cross-currency settlements. Whereas SMBs expanding internationally need affordable solutions that don't require sophisticated treasury operations.
- The Cost of Inefficiencies: Inefficient cross-border payment processes can hugely impact a business's bottom line and operations.
Hidden fees and unfavorable exchange rates can reduce payments by 3-5%, directly eroding profit margins. Payment delays disrupt cash flow and limit working capital availability, hindering business growth and daily operations. To top it, reconciliation issues create accounting headaches, consuming valuable time and resources and often requiring dedicated staff to resolve discrepancies. The cherry on the cake is compliance issues which can lead to rejected payments or regulatory penalties, adding further complications and costs.
As one IT service exporter noted: "Cross-border payments for businesses in India often come with endless fees and frustrations. Xflow has been a game-changer--streamlined, transparent and hassle-free."
What are the challenges with cross-border transactions?
Now that we’ve established how important cross-border payments are, it’s only fair to look at the challenges that come with them. Cross-border payments come with way more headaches than domestic ones. These can be anything from logistical issues (not receiving raw materials on time) to financial and trust issues (the seller requiring a letter of credit before commencing the deal) to economic issues (recession and war). All of these lead to delayed or stuck payments, long credit cycles, and regulatory and compliance roadblocks.
- Hidden Costs : High fees and FX markups are also quite a substantial burden. Traditional cross-border payments involve multiple fees, including SWIFT charges and currency conversion costs with hidden markups of 1% to 3%. Businesses also face additional taxes like GST on conversion costs, further eroding the value of money.
- Slow Transfers & Poor Visibility : Aside from the financial burden, delays and limited tracking capabilities create uncertainty and cash flow challenges. When money passes through multiple intermediary banks, it causes significant delays. SWIFT transactions typically take 2-5 days to reach the recipient's account. Companies struggle with limited visibility into where funds are during the transfer journey and face difficulty predicting exactly when the receipt will happen, complicating financial planning.
- Complex Compliance Requirements: Regulatory and compliance issues add additional layers of complexity to international transfers. Each country in the payment chain has its regulatory framework, including Anti-Money Laundering (AML) rules, Counter-terrorism financing (CTF) standards, Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements, and local reporting and documentation requirements. Navigating these complex regulations requires specialized knowledge and resources.
- Fragmented Global Infrastructure: A fragmented global payments infrastructure is infamously known to create technical obstacles. Different countries use different payment systems with limited compatibility between them and varying technological capabilities across regions. This diversification makes it difficult to create standardized, efficient processes for global transactions.
- Lack of Transparency in Transactions: Finally, the lack of transparency is another ongoing challenge for financial management. Many businesses struggle with unpredictable total costs, uncertain exchange rates, difficulty reconciling expected versus received amounts, and limited information for accounting and reporting purposes. All of this can complicate financial planning and lead to costly reconciliation efforts.
What are the different modes of cross-border payment?
Understanding the various payment methods is key to choosing the right solution for your business needs. Each method has distinct advantages and limitations, impacting transaction costs, processing times, and operational efficiency significantly.
- Bank Wire Transfers and SWIFT have long been the foundation of international banking. The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) network, an important channel partner, has been in existence for 40 years. While it is reliable for high-value transactions, it involves higher fees due to correspondent banking relationships, longer processing times (2–5 days), and limited transparency into charges and processing status. These are increasingly facing stiff competition from digital alternatives.
- Digital Wallets and Payment Platforms are modern alternatives with compelling advantages. Solutions like PayPal, Wise, and Xflow provide faster processing times, lower and more transparent fees, simpler user interfaces, and integration with business software. Smoother cross-border payments have been made possible by digital payment platforms, reducing friction and costs with accessibility to businesses of all sizes.
- Virtual Bank Account Numbers (VBANs) and Local Payouts are innovative solutions streamlining international receivables. Businesses can receive payments as if they had a local bank account in another country, convert payments to their home currency at favorable rates, and eliminate the need for multiple international bank accounts. These have helped reduce the complexity and cost of managing global payment collections significantly.
- Cards offer different options suited to specific transaction types. Some of these include credit/debit cards for C2B payments (though expensive for B2B), account-based transfers for efficient high-value B2B transactions, and eWallets, which are convenient for smaller payments and individual remittances. Selecting the appropriate payment rail can have a major impact on transaction economics.
- Letters of Credit and Documentary Collection serve specialized needs in international trade. Payment methods include Letters of Credit, which are bank guarantees of payment upon fulfillment of specified conditions, and Documentary Collection, where the seller's bank collects payment from the buyer's bank. These methods provide security for high-value commercial transactions but need expertise for effective implementation.
Comparing leading cross-border payment solutions
| Provider | Key Features | Typical Fees | Settlement Time | FX Transparency | Supported Countries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Banks | High transaction limits, established relationships | High SWIFT fees + FX markup (3-7%) | 2-5 days | Limited | Global via SWIFT |
| PayPal | User-friendly, widely accepted | 3.49% + fixed fee + FX markup | 0-2 days | Limited | 200+ countries |
| Wise | Mid-market rates, multi-currency accounts | 0.4-1.5% of amount | 0-2 days | High | 80+ countries |
| Payoneer | Multi-currency accounts, marketplace integration | 0-3% + FX markup | 1-3 days | Moderate | 150+ countries |
| Xflow | No SWIFT fees, mid-market rates, next-day settlement | 1% flat fee, no hidden markups | 1 business day | High | 140+ countries |
| Stripe | Developer-friendly, integrated with e-commerce | 1-3% + fixed fee + FX markup | 2-7 days | Moderate | 40+ countries |
Innovations & trends in cross-border payments
As the industry continues to grow, it is also constantly evolving and coming up with newer and more innovative solutions to solve the payments problem. Here are some of the current trends for us to explore:
Rise of real-time payment networks
Instant payment systems are growing at a large scale, with research expecting it to grow from 16% in 2023 to 22% of transaction volume by 2028. Funds are being made available instantly with 24/7 processing, enhanced transaction data, and improved reconciliation of accounts.
Such expansion of real-time infrastructure is also allowing businesses to have better cash flows and treasury operations. They are increasingly competing with their decades-old batch-processing systems at a rapid pace.
Localization of cross-border payments
Innovative providers are transforming international transactions by using domestic payment rails in place of SWIFT. This is made possible through virtual account numbers in different countries. Businesses can collect payments via local methods, reducing costs and speeding settlement times.
This is truly redefining the way cross-border payments usually work by treating them as connected domestic transfers rather than disjointed international wires. Localization offers specific advantages for businesses with regular payment flows in select corridors or those wanting to provide customers with familiar payment experiences.
Enhanced transparency and predictability
Modern solutions are making cross-border payments transparent with guaranteed exchange rates, upfront fee disclosure, real-time tracking, and predictable settlement times.
Businesses can manage international payments with the same confidence and predictability as domestic transactions. Prompt visibility throughout the payment journey also improves customer experience and reduces support inquiries around payment status. The good news is that the industry is increasingly moving toward standards requiring providers to disclose the total cost of payments, including exchange rate margins.
Digital public infrastructure and regulatory changes
Governments and central banks are stepping up their game by creating initiatives and regulations to make cross-border payments smoother. Popular examples include ISO 20022 standardization for richer payment data, Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) exploration, regulatory frameworks for fintech innovation, and cross-border payment system interoperability initiatives.
Going hand-in-hand with private sector innovation, these initiatives will fundamentally change the way we view cross-border payments. A recent example includes the G20's roadmap for enhancing cross-border payments to address structural challenges in international transfers through policy and technological solutions.
Key features to look for in a payment partner
Choosing the right payment partner is like getting the right wi – fi – it should be reliable and fast. It is crucial for optimizing global transactions and driving operational efficiency. Lookout for these features when choosing a cross-border payment partner:
Speed of settlement
Fast access to funds is crucial to reduce working capital requirements. Rapid settlement capabilities can transform a company's liquidity position, allowing for more efficiency in the use of funds and improved financial planning. Businesses receiving international payments frequently can particularly benefit from partners prioritizing settlement speed. Prefer solutions offering next-day or same-day settlement to enhance your financial operations.
Low-cost FX and fee transparency
Imagine earning in high value currencies and not being able to make the most of it due to fees you didn’t even know about. Hidden fees can heavily reduce the value of international payments. Choose providers that offer transparent pricing structures, disclose FX rates upfront, avoid hidden markups, and provide clear transaction fee information. Fee transparency allows businesses to accurately forecast the true cost of international operations and avoid budget surprises. Many traditional providers embed high margins in exchange rates without clear disclosure, so partners committing to transparency can offer a massive advantage.
Compliance and regulatory support
As we have seen, international payments involve complex regulatory requirements. Ideal partners should automate compliance documentation, handle reporting requirements, provide necessary paperwork like eFIRA (Foreign Inward Remittance Advice), and stay up-to-date with changing regulations. Effective compliance support reduces administrative burden and mitigates the risk of payment delays or rejections. Regulatory requirements for cross-border payments continue to evolve, making partner expertise in this area highly valuable for businesses without dedicated compliance teams.
Multi-currency and local payout support
Versatile payment solutions should support all major currencies, offer local payment methods in target markets, provide multi-currency account capabilities, and enable efficient currency management. This flexibility can make business seamless across different markets while minimizing currency conversion costs and optimizing transaction efficiency. The ability to hold balances in multiple currencies also provides strategic advantages for managing exchange rate fluctuations and timing conversions advantageously.
Developer-friendly APIs
For businesses requiring integration with existing systems, look for well-documented APIs, easy integration with accounting software, automation capabilities for recurring payments, and webhook support for real-time notifications. Strong API capabilities make workflow integration seamless, and automation reduces manual processes and potential errors. Technical documentation quality and implementation support vary a lot among providers, making this a key consideration for businesses with complex integration requirements.
How to choose the right cross-border payment provider
Selecting the optimal payment solution needs a thoughtful assessment of your business needs. Consider these factors when evaluating providers:
Business size and payment volume
Different payment solutions are tailored to different business scales. For small businesses with lower payment volumes, cost-effective, straightforward solutions may be sufficient. Larger enterprises may need systems supporting higher transaction limits, bulk payments, and automated reconciliation.
Markets served
It is important to ensure the payment solution covers all regions where your business operates or plans to expand. Some providers excel in specific corridors or regions, offering better rates or faster settlement times for particular markets. Verify that the provider supports all countries you send to and receive from.
Payment frequency and value
The frequency and size of your payments will determine the ideal solution. High-frequency, lower-value payments require efficient microtransaction handling, while occasional large transfers may prioritize favorable exchange rates and terms for high-value payments.
Integration requirements
A payment solution must be compatible with your existing systems, whether that's your ERP software, accounting system, or e-commerce platform. This ensures seamless data flow and reduces manual entry errors. Evaluate the quality of documentation and implementation support available.
Currency needs
Assess the range of currencies you need to send or receive. If you deal in multiple currencies, selecting a provider that offers competitive exchange rates across all your required currencies is essential. Consider whether you need to hold balances in multiple currencies or convert immediately.
Regulatory requirements
Choose a knowledgeable provider of the regulatory landscape in all your operating jurisdictions, ensuring your payments comply with local laws and reporting requirements.
All in all, when evaluating potential partners, consider asking these set of questions-
What are the all-in fees, including FX conversion costs?
How quickly will funds be available to the recipient?
Do senders and recipients have visibility of the transaction status?
How do you handle compliance documentation?
What currencies and countries do you support?
Can you guarantee the final amount the recipient will receive?
Red flags to watch out for
- Be cautious of providers that-
- Don't disclose their FX markup
- Have opaque fee structures
- Offer limited support options
- Can't provide clear compliance information
- Have significant negative reviews about settlement delays
Modernize your cross-border payments with Xflow
Efficient cross-border payment solutions can make all the difference to your global business operations. The right payment system can turn a common challenge into an advantage and make businesses more confident in expanding to new markets, building stronger relationships with international partners, and optimizing cash flow and working capital. It can also help reduce administrative burdens and enhance financial visibility and control.
Modern cross border payment platforms like Xflow are addressing the traditional challenges of international payments head on by eliminating SWIFT fees, offering transparent foreign exchange rates, providing next-day settlement, and automating compliance processes. Innovations like these are allowing businesses to focus more on growth than deal with the complexities of payment logistics. As you evaluate your cross-border payment needs, make it a point to prioritize providers that offer transparency, efficiency, and features most relevant to your business model. The right partner will not only help scale your business but also support your international growth journey with minimal friction!
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between SWIFT and other cross-border payment methods?
SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) is a messaging network that banks use to transmit information and instructions securely. While SWIFT itself doesn't transfer funds, it enables banks to exchange payment instructions. Alternative methods like payment platforms often use different networks, local banking relationships, or innovative technologies to move money more efficiently, typically resulting in faster transfers and lower costs.
How can I reduce the costs of international payments?
To reduce the costs of international payments, consider using specialized payment platforms compared to traditional banks, as they often offer lower fees and better exchange rates. Consolidating payments can help minimize per-transaction costs, allowing you to make fewer, larger transfers rather than multiple small ones. It's also important to choose payment providers that offer transparent foreign exchange (FX) rates so you're not hit with hidden costs. For businesses with higher transaction volumes, negotiating better rates with payment providers can lead to significant savings. Additionally, exploring local payment methods where available can help avoid expensive international transfer fees and streamline the process.
How do I ensure compliance when making cross-border payments?
When working with payment providers, it's beneficial to choose those that offer automated compliance documentation, which can save time and reduce errors. Providers that assist with regulatory requirements ensure that your business stays in line with international laws and regulations. They should also have up-to-date knowledge of changing international regulations, helping you navigate complex legal landscapes. Additionally, a good provider will generate the necessary paperwork, such as the eFIRA for Indian businesses, simplifying the compliance process and making international payments smoother.
Can I get guaranteed exchange rates for international payments?
Yes, some service providers like Xflow offer guaranteed exchange rates in partnership with global banks for specific time windows, allowing businesses to know exactly how much will be received in the local currency. This eliminates uncertainty and aids in financial planning.
How do I choose between different cross-border payment solutions?
Think about the countries you frequently send to or receive from since some providers offer better rates or services in certain regions. Also, check if the provider can integrate smoothly with your existing systems to avoid complications. Be clear about your fee tolerance, as costs can vary between providers, and ensure they can meet your settlement time requirements for timely transactions. Finally, evaluate your customer service needs, as good support is crucial for resolving any issues quickly. Once you’ve identified these factors, compare providers to find the best one that meets your business's requirements.




